What is Book Value
Book Value is the net value of a company’s assets on its balance sheet.
Book Value
In short:
The book value of a company is the value of its assets after all liabilities are subtracted, otherwise called Net Asset Value (NAV). What is important to note is that the value of the assets on a company’s balance sheet are recorded at original cost and in our calculation for book value their accumulated depreciation is subtracted away. Here is a formula to clarify.
FORMULA:
Book Value per share
In-depth:
An easy extension from total book value is to calculate the book value per share. To calculate this, simply take the total book value and divide it by the total number of outstanding common stock.
FORMULA:
The result of this equation yields some useful information to skillful investors. One piece of information is the liquidation value of the firm on a per-share basis. Another would be a comparison of how a certain company is valued relative to other like-type companies.
Book value as liquidation value:
Theoretically, this is the amount of money an investor could generally expect to receive if the company stopped operations, sold all its assets, and paid all its liabilities. However, there are a few things to consider in such a scenario.
Market value vs Book value
The first thing to consider is what is the actual market value of the assets? Remember book value is an accounting value at original cost less accumulated depreciation. Values of assets change every day, if the company has outdated technology as assets those assets may not be worth much if anything. On the other hand, if the company has buildings in areas where demand for such a building has skyrocketed the value may be much higher than the book value.
The second thing to consider, the balance sheet is a snapshot in time. Say you find a company that is trading for less than its book value if the company seems to be going out of business and your objective is to capture the liquidation value. The company may continue to operate for a long time selling off assets to postpone its ultimate failure. In this case, you lost both time and the liquidation value.
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B)
Price-to-Book (P/B) is a relative valuation metric that investors may use to compare similar companies. The calculation for P/B is to take the market cap divided by the total book value or to calculate it on a per-share basis, take the per-share price divided by the book value per share.
P/B should only be used to compare like-type companies operating in the same segment. Comparing a software company like Microsoft to a manufacturing company like Boeing would be a poor application of P/B. The reason for this lies in the number of assets it takes to produce the product they sell. Boeing takes a lot more physical assets vs Microsoft to produce their product and in turn, will have an incomparable P/B.
Where to find Book Value information
Already calculated some book value data can easily be found on many online stock data sites, we’ve included a list of a few sites below.
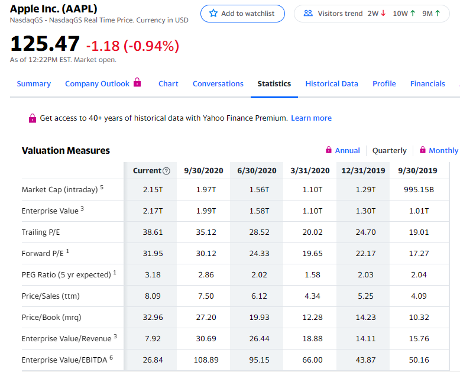
Simply visit one of these sites, enter a stock quote then look for “statistics”, “key statistics” or something to that effect. You should see “Price/Book” or “Price/Book (mrq)”. The “(mrq)” means the most recent quarter, this indicates that the figure was calculated to include the most recent quarterly data.
From the Price/Book ratio you can calculate the book value per share by dividing the current price by the P/B ratio. In the case to the right, the math would be 125.47/32.96 = ~3.85
Calculate yourself this is a bit more tricky but not much, to do this you will need to look up a company’s 10-k (annual statement) or its 10-Q (quarterly statement). Getting access to this information on publicly traded companies is easy, simply visit EDGAR: https://www.sec.gov/edgar/searchedgar/companysearch.html . This site is run by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), you can enter the company you want and it will pull all the statements. From there you will need two things, the total liabilities, and the total assets. All this information is on the Balance sheet.